Milialar : Its Causes, Symptoms and Treatment

Introduction
Milialar : Its Causes, Symptoms and Treatment, Milialar, a term gaining recognition in medical circles, refers to a rare skin condition characterized by distinctive symptoms that set it apart from more common dermatological issues. As the medical community delves into understanding Milialar, this article aims to unravel the intricacies surrounding this condition, exploring its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options.
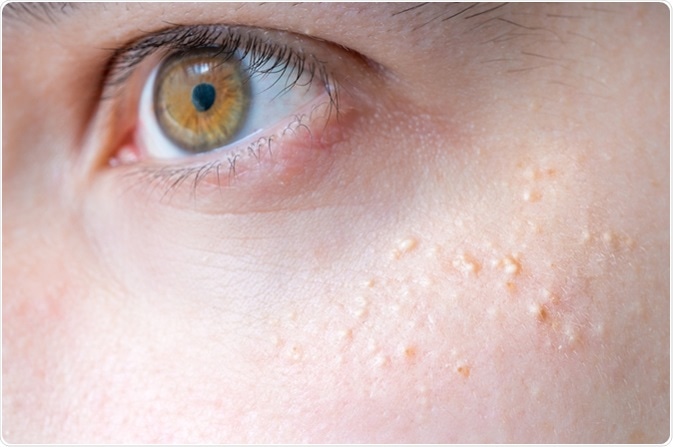
Understanding Milialar
Milialar, also known as Milia-like Idiopathic Calcinosis Cutis, is a skin disorder marked by the formation of small, firm, white or yellowish nodules on the skin. These nodules, often referred to as milia-like cysts, are composed of calcium deposits within the dermis. Milialar is considered a rare condition, and its exact etiology remains a subject of ongoing research.
Must Read=The Mysteries of Brown Mystery Snails Need You Know
Causes of Milialar
The precise causes of Milialar are not fully understood, contributing to the complexity of its diagnosis and management. However, several factors are believed to be associated with the development of milia-like cysts:
- Calcium Dysregulation: Milialar is characterized by the abnormal deposition of calcium within the skin. Dysregulation in calcium metabolism, where there is an imbalance between calcium absorption, utilization, and excretion, is considered a potential contributing factor.
- Genetic Predisposition: There is evidence to suggest that Milialar may have a genetic component. Individuals with a family history of skin disorders or conditions related to calcium metabolism may have an increased susceptibility to developing milia-like cysts.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain underlying medical conditions have been linked to the development of Milialar. These include disorders affecting calcium metabolism, such as pseudohypoparathyroidism, and conditions associated with connective tissue abnormalities.

Symptoms of Milialar
The primary manifestation of Milialar is the appearance of small, white or yellowish cysts on the skin. These cysts are typically painless and may vary in size, ranging from pinpoint lesions to larger nodules. Common locations for Milialar cysts include the face, particularly around the eyes and cheeks, although they can occur on other areas of the body.
Key symptoms of Milialar include
- Small, Firm Cysts: Milia-like cysts present as small, firm bumps on the skin. Their appearance is often likened to milia, which are tiny cysts filled with keratin that commonly occur in infants.
- White or Yellowish Color: The cysts associated with Milialar tend to have a white or yellowish color. This coloration is due to the presence of calcium deposits within the cysts.
- Painless Lesions: Milialar cysts are typically painless and do not cause discomfort. Unlike some skin conditions that may be accompanied by itching or tenderness, Milialar often goes unnoticed until the characteristic cysts are observed.
- Variable Size: Milia-like cysts can vary in size, with some appearing as tiny pinpoint lesions and others developing into larger nodules. The size and distribution of the cysts can influence the overall presentation of the condition.
Diagnosis of Milialar
Diagnosing Milialar involves a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history assessment, and, in some cases, additional diagnostic procedures. The distinctive appearance of milia-like cysts is often a key factor in diagnosis. Dermatologists may consider the following steps in diagnosing Milialar:
- Clinical Examination: A dermatologist will conduct a thorough examination of the skin to assess the presence of milia-like cysts. The distribution, size, and color of the cysts play a crucial role in distinguishing Milialar from other skin conditions.
- Medical History: Understanding the patient’s medical history is essential in identifying potential underlying factors or genetic predispositions that may contribute to the development of Milialar.
- Skin Biopsy: In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis. A small sample of tissue is taken from a milia-like cyst for microscopic examination, helping to rule out other skin conditions and providing insights into the nature of the cysts.
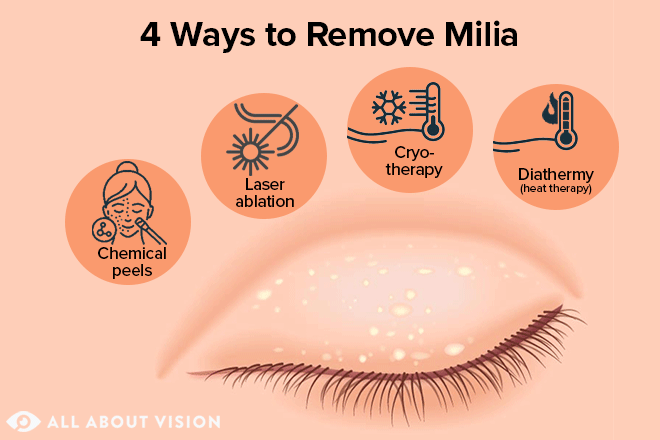
Treatment Options for Milialar
The management of Milialar is tailored to the individual, considering factors such as the extent of cyst formation, associated symptoms, and underlying medical conditions. While Milialar is generally benign, treatment options may be explored for cosmetic reasons or if the cysts are causing discomfort. Common approaches include:
- Observation: In many cases, Milialar may be asymptomatic, and the cysts pose no medical concern. In such instances, a “watch and wait” approach may be recommended, with regular monitoring to assess any changes in the condition.
- Topical Treatments: Topical treatments, such as retinoids or exfoliating agents, may be prescribed to promote the shedding of dead skin cells and help prevent the formation of new milia-like cysts. These treatments are aimed at improving skin texture and reducing the recurrence of cysts.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Dermatological procedures, such as laser ablation, microdermabrasion, or chemical peels, may be considered to address milia-like cysts. These procedures aim to exfoliate the skin and remove the cysts, enhancing the overall appearance of the skin.
- Cryotherapy: Cryotherapy involves the use of liquid nitrogen to freeze and remove milia-like cysts
Conclusion
Topical treatments, such as retinoids or exfoliating agents, may be prescribed to promote the shedding of dead skin cells and help prevent the formation of new milia-like cysts. These treatments are aimed at improving skin texture and reducing the recurrence of cysts.



